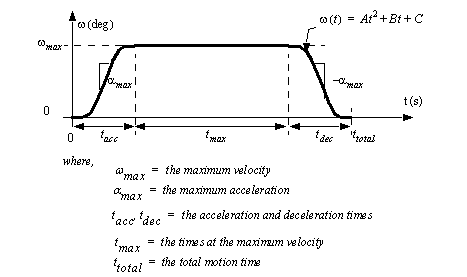
Ideal Acceleration And Deceleration Formula

Any time there is a change in velocity or the direction of motion acceleration has occurred.
Acceleration and deceleration formula. Deceleration also known as retardation or negative acceleration is the acceleration acts in the opposite direction of motion and is responsible for reducing the velocity of a body. Acceleration is the change in velocity during a given period of time. Acceleration- Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time.
Deceleration final velocity -. The formula for acceleration can be used recognizing that the final result must have a negative sign. We can easily define acceleration as change in velocityAs you understood from the definition there must be change in the velocity of the object.
Deceleration is a special case of acceleration whereby it only applies to objects slowing down. In a physics equation given a constant acceleration and the change in velocity of an object you can figure out both the time involved and the distance traveled. Deceleration is the opposite of acceleration.
The formula for acceleration can be used here with a negative sign to identify the deceleration value. This is the most common equation used to calculate acceleration torque for all types of motors. Acceleration happens when an unbalanced force acts on an object causing it to change speeds towards the direction the force is pushing or.
Just like acceleration deceleration is calculated by taking the difference between the initial and final speeds divided by the time it took the object to change speed. It is denoted by symbol a and is articulated as- The SI unit for acceleration is. SI unit for measuring velocity is meter per second ms.
Acceleration is a vector which means that it has to be reported as a magnitude with a direction. Mathematically acceleration torque is made up of load inertia and acceleration rate as shown below. If starting velocity final velocity and time taken are given Deceleration Formula is given by It is the final velocity minus the initial velocity with a negative sign in the result because the velocity is decreasing.