Amazing Acid Rain Limestone Equation

How does acid precipitation affect marble and limestone buildings.
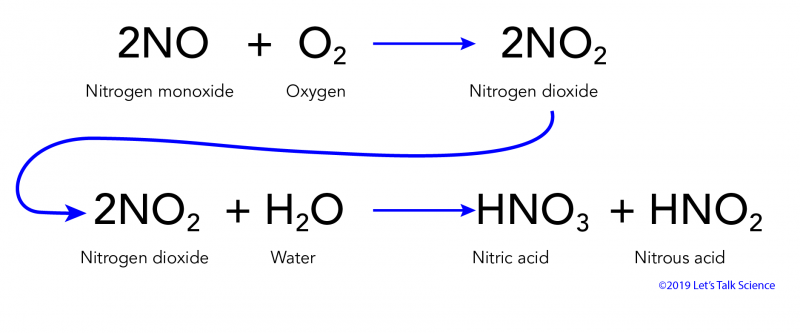
Acid rain limestone equation. Acid rain has the following reaction with the marble calcium carbonate. Sulfur dioxide water - sulfurous acid sulfur trioxide water - sulfuric acid nitrogen dioxide water - nitric acid nitrous acid. The chemical equation that is going to be followed throughout the experiment will be.
Acid Rain And Limestone Chemical Equation. Limestone and marble slowly dissolve in the presence of H ions. Stone Buildings and Monuments in Acid Rain Marble and limestone have long been preferred materials for constructing durable buildings and monuments.
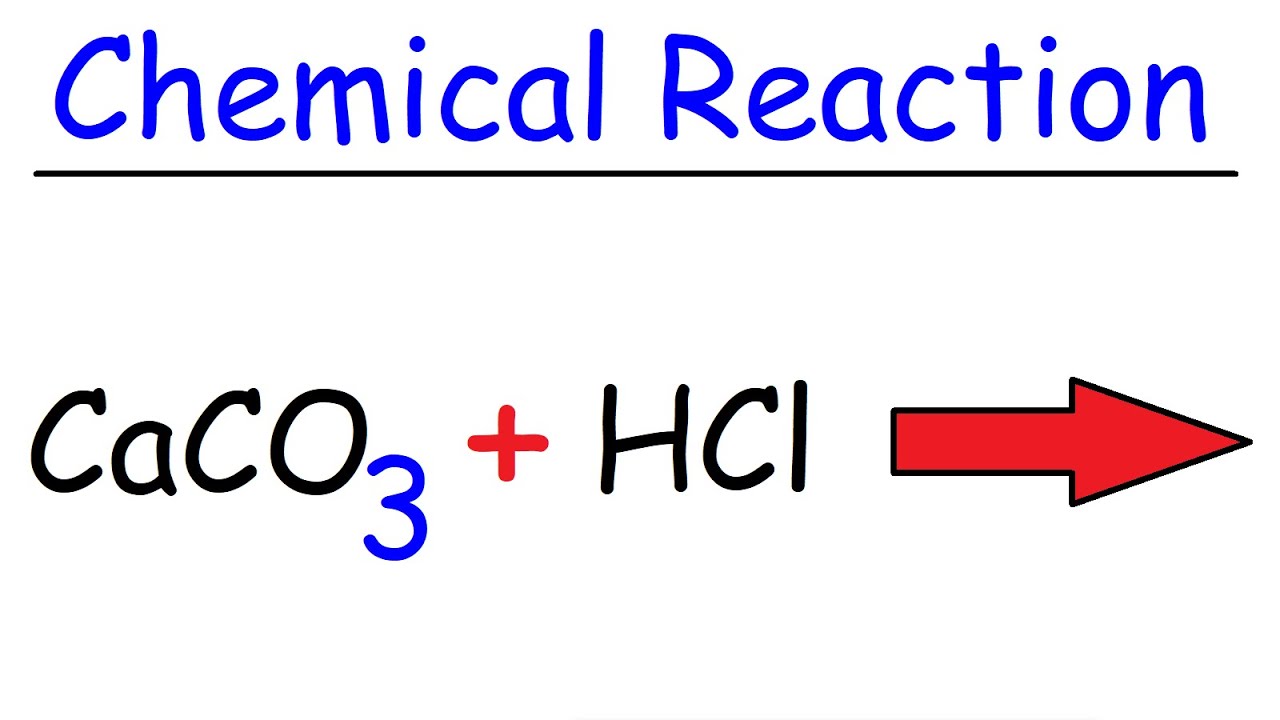
Atmospheric pollutants are easily moved by wind currents so acid-rain effects are felt far from where pollutants are generated. CaCO 3 s 2HClaq CaCl 2 aq H 2 Ol CO 2 g. Rain water in equilibrium with atmospheric C0 2 at STP has a pH of 56.
But if you add an acid you add hydrogen ions H which will react with the carbonate to form hydrogen carbonate HCO3- ions which are very soluble in water and the limestone will dissolve. This is due to the presence of sulphurous acid sulphuric acid and nitric acid in rain water. Acid rain contains carbonic acid nitric acid and sulphuric acid CO2 NO2 and SO2.
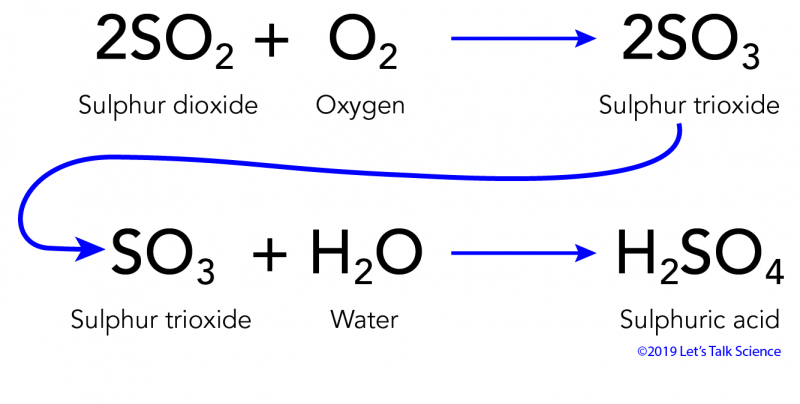
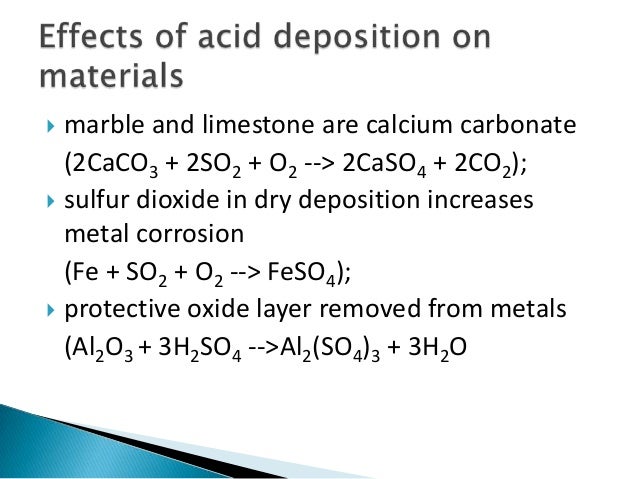
Theory Natural Weathering versus the Incremental Effect of Acidic Deposition. With the advent of acid rain many of the existing buildings and monuments composed of limestone and marble are being corroded away by the reaction below. 2SO 2 g O 2 g 2H 2 O I 2H 2 SO 4 aq Acid rain occurs when the pH of rain water falls between 20 to 55.
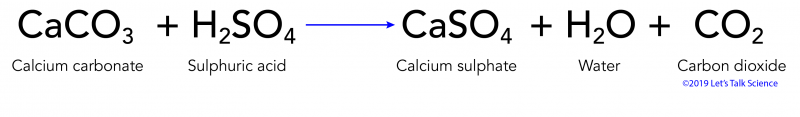
A Limestone contains calcium carbonate. CaCO3s H2SO4aq -- Ca2aq SO4-2aq H2O CO2. Were being asked to write an equation on how sulfuric acid will react with marble and limestone.