Ideal Anaerobic Respiration Function

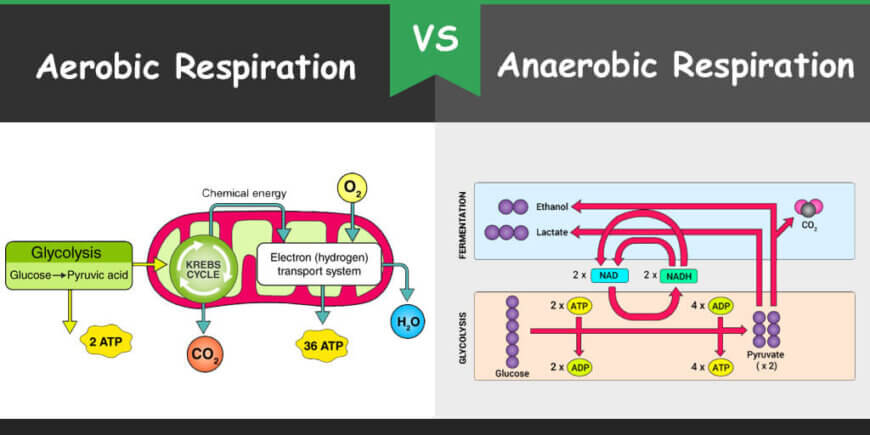
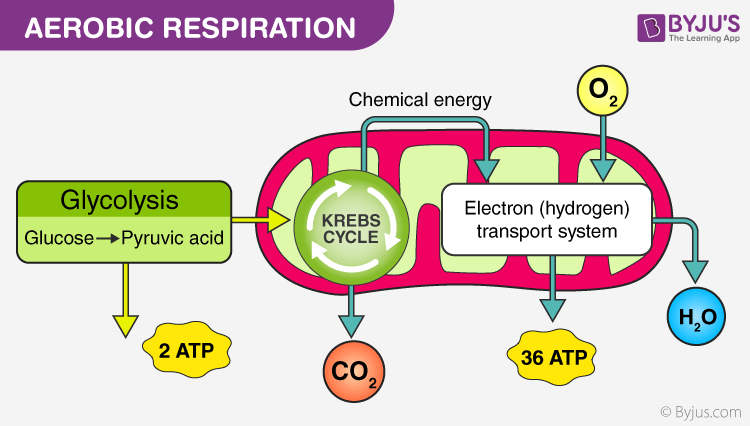
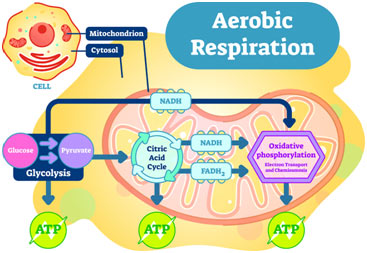
Aerobic respiration as the name suggests is the process of producing the energy required by cells using oxygen.
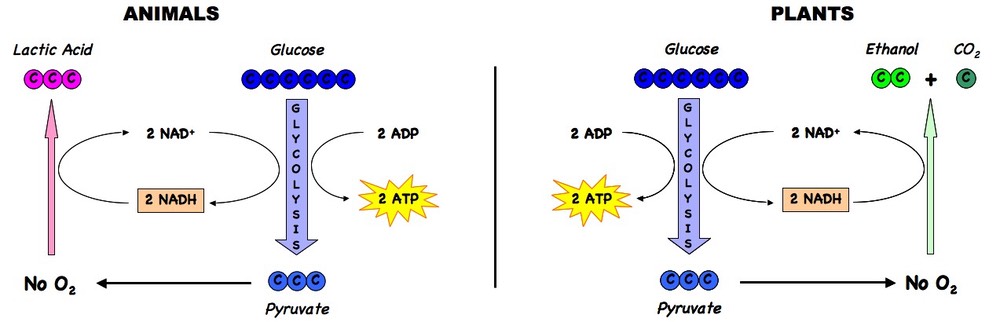
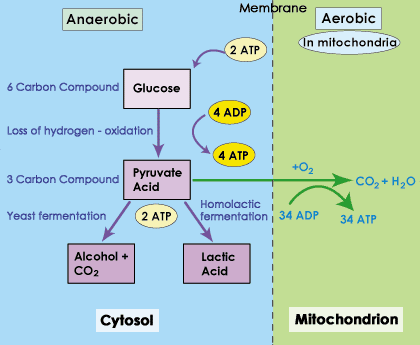
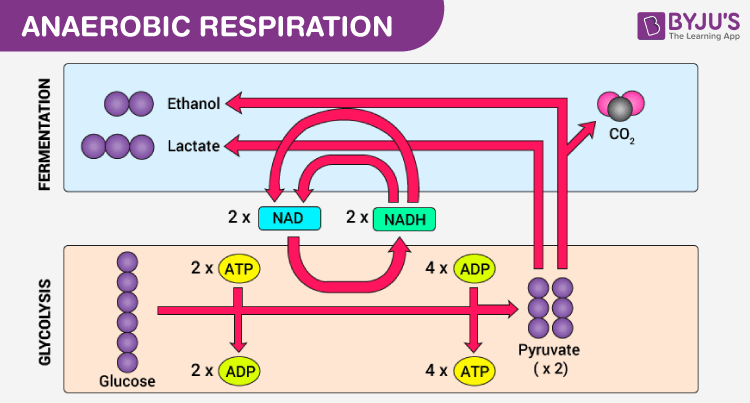
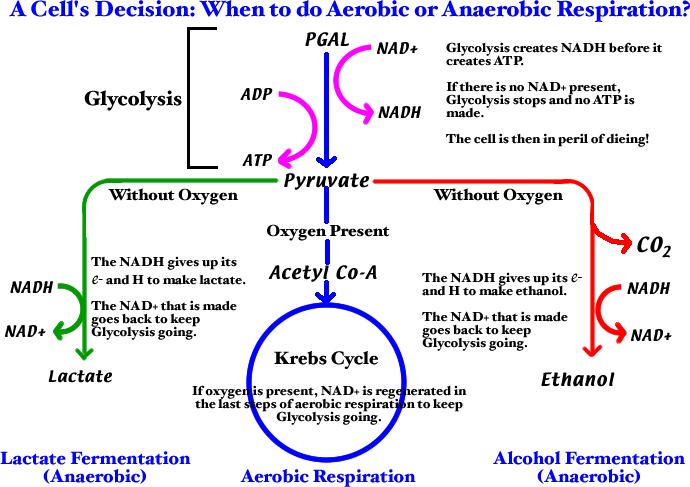
Anaerobic respiration function. Anaerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration does not need oxygen unlike aerobic respiration. The anaerobic respiration definition states that it is the pathway where the glucose is broken down into molecules in the absence of oxygen to produce energy. Sometimes the body cant supply the muscles with the oxygen it needs to create energy such as in a sprinting situation.
Without the process of anaerobic respiration there may be no energy supplied to muscles in times of high demand. Respiration is used by all cells to turn fuel into energy that can be used to power cellular processes. On the other hand the anaerobic respiration is when respiration happens in the absence of oxygen.
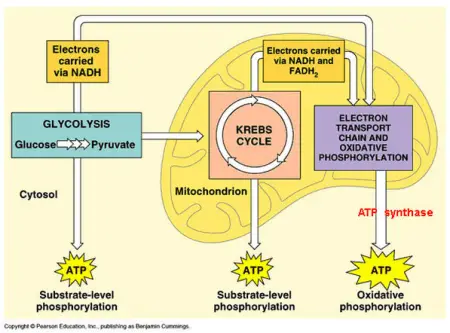
Anaerobic respiration is the process of creating energy without the presence of oxygen. The first step in all cellular respiration pathways is glycolysis that takes place without the presence of molecular oxygen. Anaerobic respiration is the process of producing cellular energy without oxygen.
At the end of anaerobic respiration 2 molecules of ATP are produced. This is in contrast to the highly efficient process of aerobic respiration which relies on oxygen to produce energy. Anaerobic respiration happens in the cytoplasm where glycolysis releases energy from glucose and fermentation recycles NADH back to NAD.
This might occur if youre pushing your limits during an aerobic activity like spinning or a cardio workout and the oxygen supply to your muscles is insufficient to maintain aerobic-only respiration. Aerobic respiration produces far more ATP but risks exposure to oxygen toxicity. The chemical reaction transfers energy from glucose to the cell.
One of the best examples of anaerobic respiration is the process of fermentation in yeast. This process occurs mostly in microorganisms but it. Anaerobic respiration is a relatively fast reaction and produces 2 ATP which is far fewer than aerobic respiration.