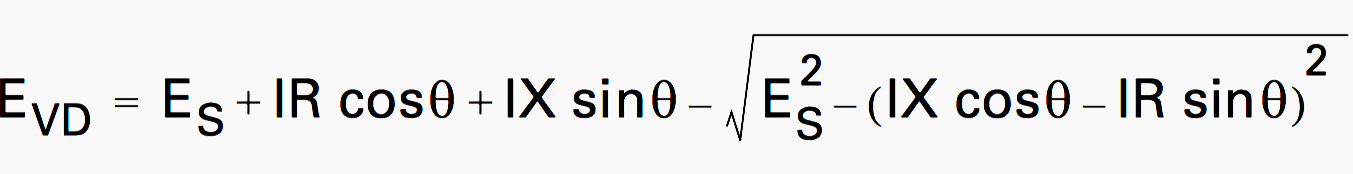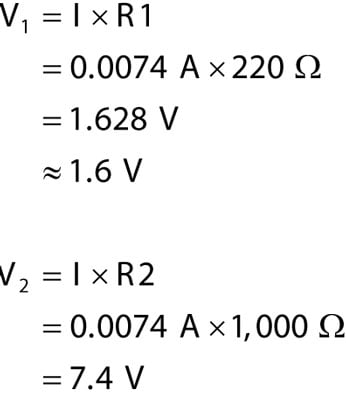Supreme Voltage Drop Equations

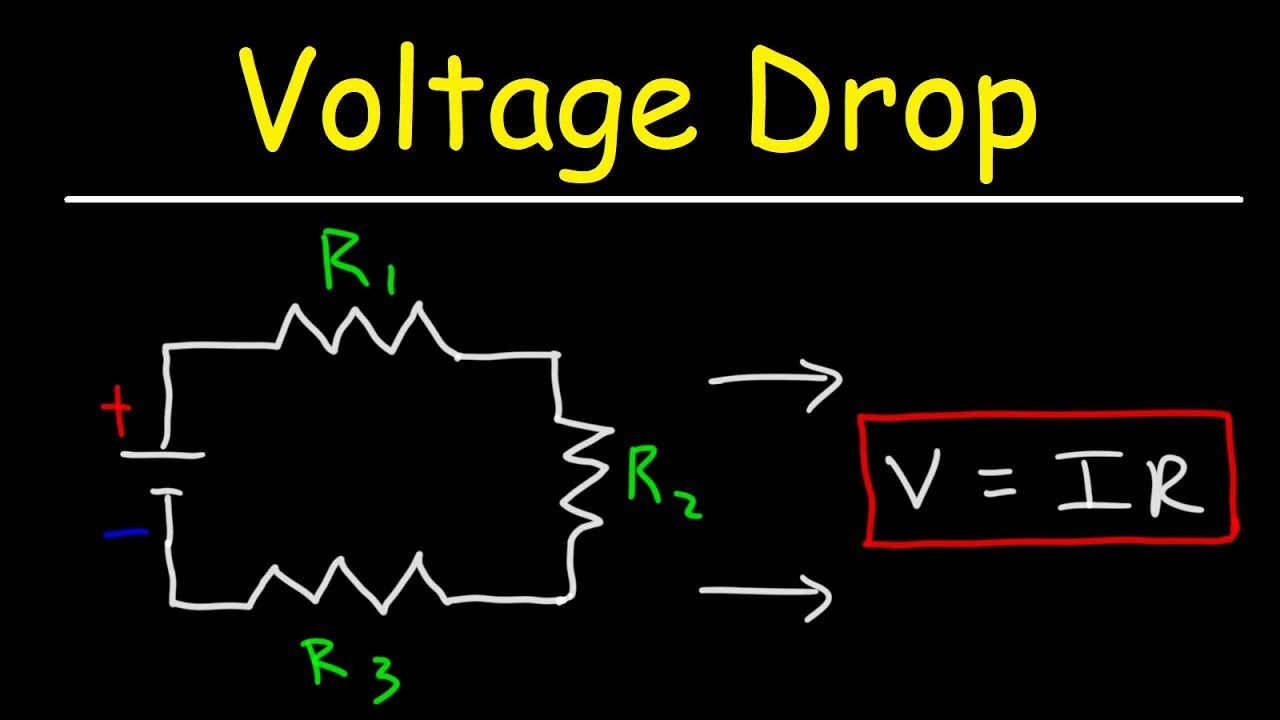
In simple words the voltage drop is the arithmetical difference between a higher voltage and a lower voltage.
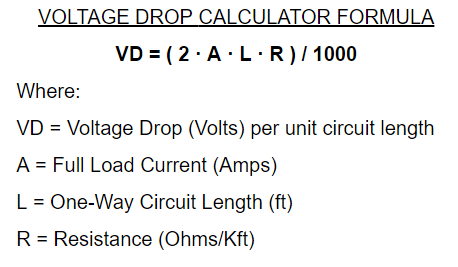
Voltage drop equations. There is a myth that calculating volt drop with electrical code is difficult. VD The voltage drop of the circuit in volts. L Length of the circuit from power supply to load.
In addition the amount of energy per second power delivered to a component in a circuit is equal to the voltage drop from corner to corner of that components terminals multiplied by the current flow through the components. 2 x 0866 x 200 ft x 11 ohms x 20A 76208 Dividing 7621 by 1000 ft gives a voltage drop of 77V. The voltage drop is the amount of electrical potential voltage loss caused by the contrary pressure of the wire.
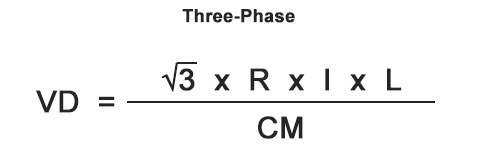
This is done by 240 volts x 2 or 48 Voltage Drop. In other words Vd I x R. VD 2 x K x Q x I x DCM - Single Phase VD 1732 x K x Q x I x DCM - Three Phase.
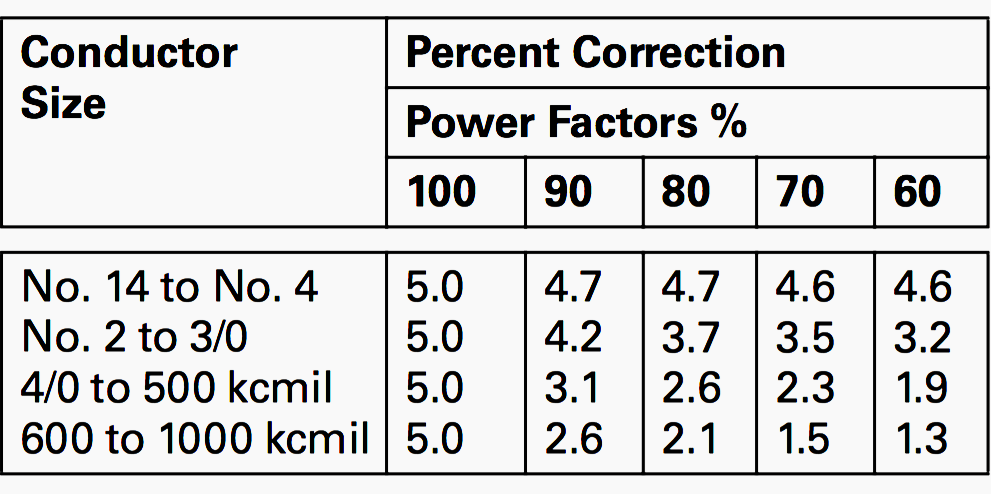
Boost the length to 500 ft and that No. Voltage drop is calculated using the most universal of all electrical laws. In a parallel circuit the voltage drop across each resistor will be the same as the power source.
Total length of conductor. DC single-phase voltage drop calculation dc voltage drop formula The voltage drop V in volts V is equal to the wire current I in amps A times 2 times one-way wire length L in feet ft times the wire resistance per 1000 feet R in ohms Ωkft divided by 1000. In a series circuit the voltage drop across each resistor will be directly proportional to the size of the resistor.
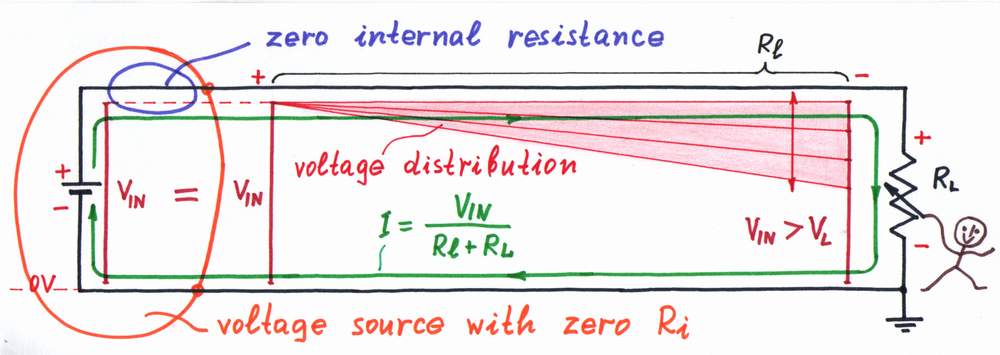
This states that the voltage potential across the conductor is equal to the current flowing through the conductor multiplied by the total resistance of the conductor. The voltage drop formula for 3 phase systems is the following. Kirchoffs Voltage Law KVL - states that the sum of voltage drop around any closed path in a circuit is zero.