Amazing Circular Motion Acceleration Formula

Race cars with constant speed around curve.
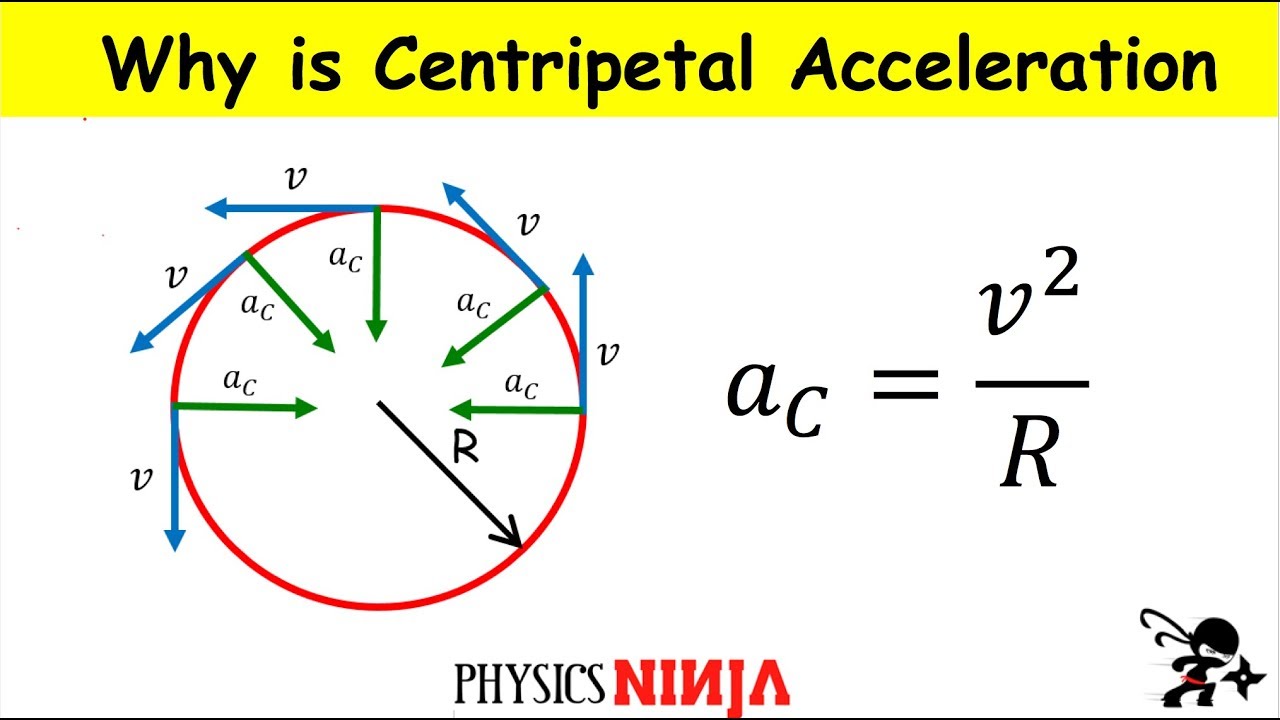
Circular motion acceleration formula. Circular Motion Tangential Angular Acceleration v t rω The arc length s is related to the angle θin radians rad as follows. The acceleration is directed towards the centre of the circular path. Thus the magnitude of the acceleration is v 2 r and its direction is along the radius and the negative sign indicates that it is opposite to the radius vector ie.
What I want to do in this video is a calculus proof of the famous centripetal acceleration formula that tells us the magnitude of centripetal acceleration the actual direction will change its always going to be pointing inwards but the magnitude of. Since the average acceleration is along Δv aΔvΔt the average acceleration is perpendicular to Δr. Endgroup user203191 Sep 7 18 at 1151.
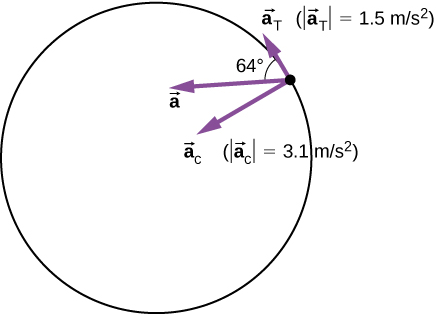
Thus a particle in circular motion with a tangential acceleration has a total acceleration that is the vector sum of the centripetal and tangential accelerations. F mv 2 r mω 2 r. Go through the Cheat Sheet of Circular Motion and be familiar with different sub-topics like Newton Equation in Circular Motion Centripetal Force Net Acceleration etc.
Ac v2r a c acceleration centripetal ms 2. The rotation around a fixed axis of a three-dimensional body involves circular motion of its parts. To help you learn the concept of Circular Motion better we have listed the Circular Motion Formulas in an efficient manner.
Uniform Circular Motion Examples. In equation form angular acceleration is expressed as follows. This acceleration is called the centripetal acceleration.
The acceleration vectors are shown in Figure 45. It is perpendicular to the linear velocity v and has the magnitude ac v2 rac rω2 a c v 2 r. It can be uniform with constant angular rate of rotation and constant speed or non-uniform with a changing rate of rotation.